Regression Problems
Regression is used to derive relationship between variables. If there are 2 variables then its called “Bi-Variant” data. If there are more than 2 variables, they are “Multi-Variant” data. By deriving this relationship, it will be used for predicting the value of one variable (Dependent variable) based on other variables (Independent variables).
- Regression allows you to measure either influence of one or more variables on a dependent variable OR
- Allows you to predict the value of a dependent variable based on the values of one or more dependent variable
Linear Regression
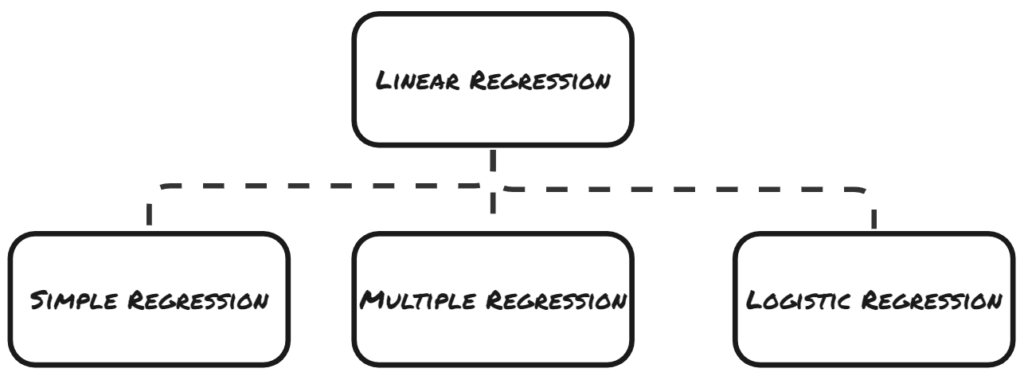
- Both Simple and Multiple Linear Regression analysis is done when, the dependent variable is a metric (or continuous).
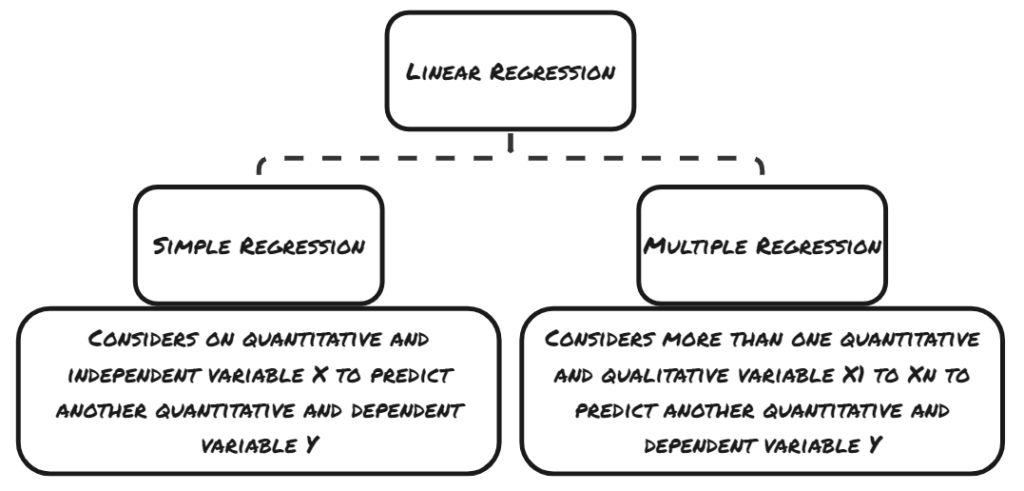
(a) Simple Linear Regression
- In the simple linear regression, you have one dependent and one independent variable.
- The basic form of regression is the linear regression.
- It is in the form of Y = B0 + B1X + e, where ‘Y’ is the dependent variable and ‘X’ is the independent variable.
- The relationship between the 2 variables can be plotted on a single line.
- Examples of linear regression analysis include, predicting the house price vs house square-footage or between hours spent learning vs marks scored.
(b) Multiple Linear Regression
- In multiple Linear Regression, you have single dependent variable, but multiple independent variable.
(c) Logistic Regression
- logistic regression is a type of linear model.
- Despite its name, logistic regression is used for binary classification problems, where the goal is to predict the probability that an instance belongs to a particular class (e.g., 0 or 1).
- The logistic function (also called the sigmoid function) is used to map the linear combination of input features to a value between 0 and 1, representing the probability.

- Logistic Regression is used when you have a categorical dependent variable. i.e. when you have yes or no answers you have logistic regression.
- for example whether a person will buy the product or not?
Non-Linear Regression
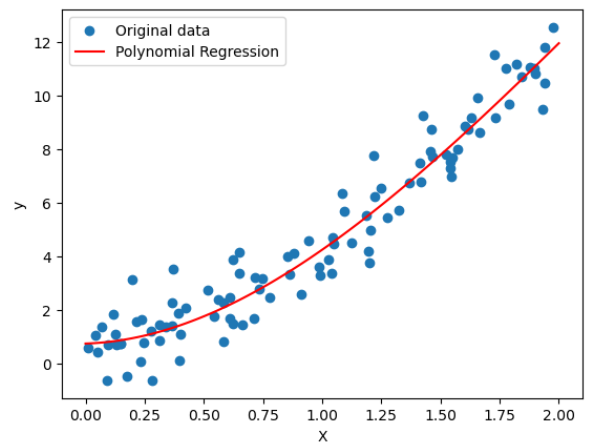
Polynomial Regression
- Polynomial regression is a type of regression analysis in which the relationship between the independent variable (input) and the dependent variable (output) is modeled as an nth-degree polynomial. In other words, instead of fitting a linear equation to the data, as in simple linear regression, polynomial regression uses a polynomial equation of higher degree.
- The general form of a polynomial regression equation is:

Sample Code
import numpy as np
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
from sklearn.preprocessing import PolynomialFeatures
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# Generate some sample data
np.random.seed(42)
X = 2 * np.random.rand(100, 1)
y = 3 * X + 1.5 * X**2 + np.random.randn(100, 1)
# Split the data into training and testing sets
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.2, random_state=42)
# Transform the features to include polynomial terms up to degree 2
poly_features = PolynomialFeatures(degree=3, include_bias=False)
X_train_poly = poly_features.fit_transform(X_train)
# Fit a linear regression model to the polynomial features
poly_reg = LinearRegression()
poly_reg.fit(X_train_poly, y_train)
# Visualize the results
X_range = np.linspace(0, 2, 100).reshape(-1, 1)
X_range_poly = poly_features.transform(X_range)
y_range_pred = poly_reg.predict(X_range_poly)
plt.scatter(X, y, label='Original data')
plt.plot(X_range, y_range_pred, color='red', label='Polynomial Regression')
plt.xlabel('X')
plt.ylabel('y')
plt.legend()
plt.show()
Classification Problems
In classification problems, the data is classified into 2 or more discrete categories. If it is into 2 categories, then it is called “Binary” or if it is into more than 2 then it is called “Multi-Class”.
