What is an API?
An API (Application Programming Interface) is a set of rules and protocols for building and interacting with software applications. It defines the methods and data structures that developers can use to interact with an application, service, or system, allowing different software systems to communicate with each other.
Key Points about APIs:
Web APIs: Web APIs are APIs that are accessed over the web using HTTP/HTTPS protocols. They are widely used for web services, enabling web applications to communicate with external services like social media platforms, payment gateways, and more.
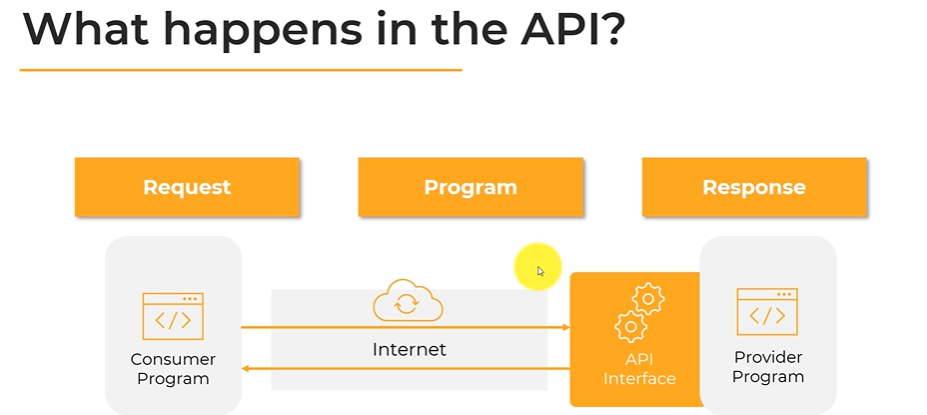
Intermediary: An API acts as an intermediary between two applications, enabling them to exchange data and functionalities seamlessly.
Defined Methods: APIs provide a set of defined methods or endpoints that developers can use to request and send data. These methods are typically associated with HTTP verbs like GET, POST, PUT, DELETE, etc.
Data Structures: APIs specify the data structures (such as JSON or XML) that applications use to send and receive data. This ensures that both the sending and receiving applications understand the data being exchanged.
Abstraction: APIs abstract the underlying implementation details of the software, providing a simpler interface for developers to interact with. This allows developers to use the functionality without needing to understand the internal workings of the application.
Integration: APIs are essential for integrating different systems, allowing them to work together and share data. For example, a weather application might use an API to fetch weather data from a weather service provider.
| Tool / Concept | Use Case |
|---|---|
| REST APIs | Partner integrations, customer registration flows, CRM updates, CDP sync. |
| Webhook & Token Management | Freshdesk, Carnival, WhatsApp Bot CDP data push. |
| Azure (Tokens, IP Whitelisting) | Security and infrastructure for integrations. |
