All About APIs
API Application Programming Interfaces. It is a software intermediary that allows 2 applications to talk to each other. API is like a messenger. There is a message that you need to send to a server such as a website or mobile application. Similarly if this server, i.e. website or application is trying to send you a message, it will use an API.
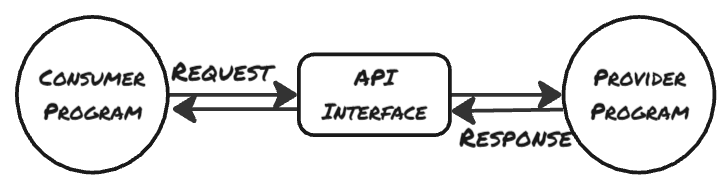
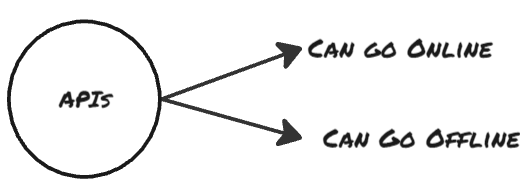
- The requests can go online as well as offline.
- Eg. of Offline mode of API Request – Camera sending pictures to Photo Editor within your mobile phones.
What is a Web Service ?
- An API that goes Online is termed as a webservice.
- Web Services are a subset of APIs. i.e. All Web Services are APIs but not all APIs are Web Services.
Data Types for APIs
- While sending an API request online, you can send it with data in 2 types:
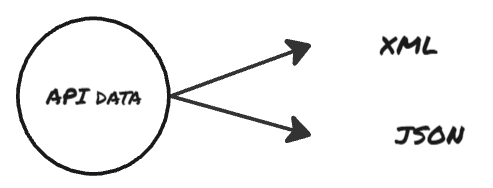
- Each type of data has a different protocol for transit.
Protocols for Data Transit
- HTTP of Hyper Text Transfer Protocol, is used to transfer data through internet.
- APIs are all about transferring data b/w 2 applications or 2 servors.
- For online APIs/Webservices the protocol used to transfer data is called HTTP
- Hence communication between client computers and web servers is done by sending HTTP requests and receiving HTTP responses.
- Clients are mostly browsers, programs or devices and servers are mostly computers in the cloud.
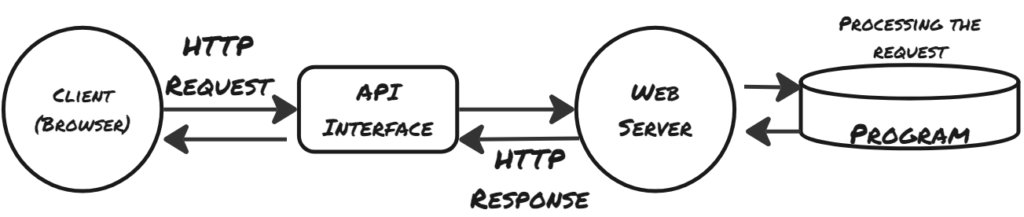
Steps in Communication
- Client ( e.g. a browser) sends an HTTP request to the web.
- A web server receives the request.
- The server runs an application to process the request.
- The server returns an HTTP response (O/P) to the browser.
- The client (the browser) receives the response.
- When the client communicates to the server, there are many methods for this communication called HTTP methods.
- There are mainly over 10 methods, out of which the main methods include – GET, POST, PUT, DELETE which are in line with the CRUD operations
Methods
- C: Create: POST: Submit data to Server
- R: Read: GET: Retrieve data from Server
- U: Update: PUT: Update data already on Server
- D: Delete: DELETE: Deletes data from Server
- The method is specified while you are sending the request, not as a response.
HTTP Status Codes (Responses)
- 2XX: The request was successfully received, understood and accepted.
- 4XX: Problem with client. e.g. accessing a page that doesn’t exist.
- 5XX: Problem with server. e.g. Too many people accessing a website, causing the site to crash and unable to fulfill requests.
While sending an API request, say a ‘POST’ request, you are sending some data with request. Similarly, while receiving a response from the server, the response will also include data in it. The data that is sent in request or response is of 2 types: XML and JSON.
XML – Extensible Markup Language
- It is a markup language like HTML.
- It is created by WEC, the same organization that created HTML.
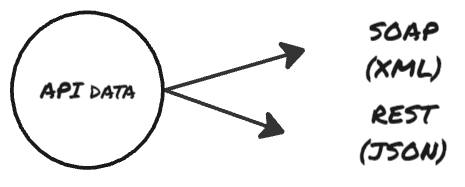
- To send XML data, we use SOAP API. These are older APIs, and SOAP stands for – Simple Object Access Protocol. Here is an example ->
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<library>
<book>
<title>The Great Gatsby</title>
<author>F. Scott Fitzgerald</author>
<year>1925</year>
<genre>Fiction</genre>
</book>
<book>
<title>To Kill a Mockingbird</title>
<author>Harper Lee</author>
<year>1960</year>
<genre>Fiction</genre>
</book>
<book>
<title>A Brief History of Time</title>
<author>Stephen Hawking</author>
<year>1988</year>
<genre>Non-Fiction</genre>
</book>
</library>
JSON: Java Script Object Notation
- It is built using JavaScript
- JSON code is smaller than XML
- JSON code data is send using REST APIs.
- REST – Representation State Transfer.
- In JSON there are 3 main components:
- Strings: Described in double quotes – “ABCD”
- Lists: Described with square brackets – [1,2,3]
- Objects: Collection of key value pairs, Described with Curly Brackets – {“Key”:”value”}
- Sample of JSON code
{
"library": [
{
"title": "The Great Gatsby",
"author": "F. Scott Fitzgerald",
"year": 1925,
"genre": "Fiction"
},
{
"title": "To Kill a Mockingbird",
"author": "Harper Lee",
"year": 1960,
"genre": "Fiction"
},
{
"title": "A Brief History of Time",
"author": "Stephen Hawking",
"year": 1988,
"genre": "Non-Fiction"
}
]
}
Testing APIs
- Software testing validates APIs functioning.
- API testing is done on the business logic layer and not on UX part.
- Purpose of API testing:
- Functionality
- Reliability/ Repeatability
- Performance
- Security
API Documentation
- Technical content deliverable with instructions on how to use and integrate the API
- Since everything has APIs, documentation is needed to keep track of them as well as to increase adoption.
Other Important Points
- Difference between Patch and PUT
- Put is used to modify resources where the client sends data that updates the entire record.
- e.g. you cannot send only the User ID or Password. you have to send them together.
- Patch is used for partial update of records.
- .

